
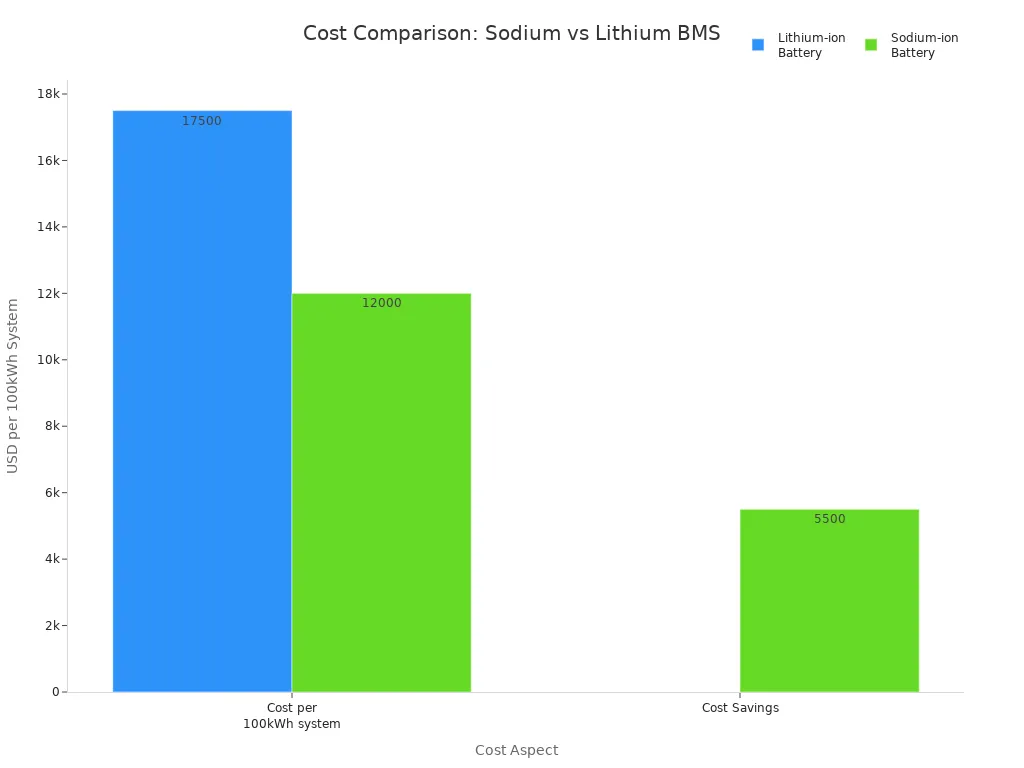
Sodium battery BMS is the cheaper option for 2025. Sodium is easy to find in the Earth’s crust, which makes its raw material cost lower and more steady than lithium. Lithium is rare, and its price fluctuates significantly. The table below highlights the main differences between lithium-ion battery BMS and sodium-ion battery BMS:
Aspect | Lithium-ion Battery BMS | Sodium-ion Battery BMS |
|---|---|---|
Raw Material Cost | High because lithium and cobalt are rare and prices change | Lower because sodium is common and supply is steady |
Current Collector Material | Uses copper, which costs more | Uses aluminum, which costs less |
Use of Cobalt/Nickel | Needs these metals, which adds cost | Usually does not need them, so costs less |
Cost per kWh at scale | $10,000 - $14,000 for each 100kWh system | |
Cost Savings | Not available | Saves $5,000 - $6,000 for each 100kWh system |
Supply Chain Stability | Prices and supply can change quickly | Prices are steady and materials are easy to get |
Sodium-ion technology is increasingly used for home and business energy storage. Governments and companies invest in sodium-ion batteries because they cost less and have a stable supply chain. These batteries are easy to produce in large quantities and offer a greener choice. Meanwhile, lithium battery BMS remains a key technology but comes with higher costs and supply challenges. Many homeowners and businesses choose sodium-ion battery BMS to have reliable, affordable, and eco-friendly power solutions.
Sodium battery BMS costs less than lithium battery BMS. It uses cheaper and more common materials like sodium and aluminum. It does not use rare metals like lithium, cobalt, or nickel.
Sodium battery BMS has steady prices and supply. This makes it a good choice for homes and businesses. It works well in cold places too.
Lithium battery BMS has more energy and lasts longer. This makes it better for portable devices and electric cars. But it costs more and is harder to get.
Sodium battery BMS is safer because it handles heat better. It uses materials that do not catch fire easily. This lowers fire risks and safety costs.
Sodium battery BMS is better for the environment. It is easier to recycle and mining is less harmful. This helps support green energy solutions.
When you look at sodium battery BMS and lithium battery BMS, the materials matter a lot for the first price you pay. Sodium battery BMS uses aluminum for its current collectors. Aluminum is much cheaper than copper. Lithium battery BMS uses copper, which costs more. Copper can cost three to four times more than aluminum. This makes sodium battery BMS cheaper at the start.
Sodium battery BMS does not use cobalt or nickel. These metals are rare and cost a lot. Lithium battery BMS needs cobalt and nickel, which makes it more expensive. Sodium is over 500 times more common than lithium. This helps keep the price of sodium battery BMS low and steady.
Sodium-ion batteries use aluminum, which costs less than copper.
Copper is three to four times more expensive than aluminum.
Sodium-ion batteries do not need cobalt or nickel, which are rare and costly.
Sodium is much easier to find than lithium, so prices stay low.
Not using cobalt and nickel in sodium battery BMS lowers cost and supply risks.
Because of these choices, sodium battery BMS usually costs less at the start than lithium battery BMS. For big projects or home energy storage, this can save a lot of money right away.
The value of a battery management system over time is about more than just the first price. You also have to think about fixing, replacing, and how easy it is to get the parts.
Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
Raw Material Concentration | Lithium, cobalt, nickel, manganese, graphite are found in only a few places. |
Key Raw Material Sources | Over 70% of cobalt comes from the Democratic Republic of Congo. Lithium mostly comes from South America, Australia, and China. |
Refining Capacity | China processes over 60% of the world’s lithium and almost 70% of cobalt. |
Price Impact | Lithium prices went up over 400% in 2022–2023, making batteries cost more. |
Geopolitical Risks | Political problems and trade rules can change supply fast. |
Environmental & Social Constraints | New mining projects have strict rules and social worries. |
Sodium-ion Battery Advantage | Uses more common and cheaper sodium, which lowers costs. |
Lithium battery BMS can have problems if there are not enough materials or if prices go up. Most lithium, cobalt, and nickel come from just a few countries. If something happens in those places, prices can rise quickly. For example, lithium prices went up by over 400% in one year. This makes it hard for companies to plan and keep prices low.
Sodium battery BMS does not have these problems. Sodium is easy to find and cheap. Aluminum, used in sodium battery BMS, is also easy to get. This means the price of sodium battery BMS stays steady over time. Companies and homeowners can expect stable costs and fewer surprises.
Sodium battery BMS also needs less fixing and has fewer parts that break fast. This means you do not have to replace or repair it as much. Over time, these savings make sodium battery BMS a good choice for long-term value.
Note: More people want electric vehicles, so there may not be enough lithium and other key materials by 2027. Sodium battery BMS helps avoid these problems by using materials that are easy to find.
Energy density means how much energy a battery can store for its size or weight. This is important for things like phones and electric cars. These devices need batteries that are small and light. The table below shows how much energy sodium-ion and lithium-ion batteries can hold in 2025:
Battery Type | Average Gravimetric Energy Density (Wh/kg) in 2025 |
|---|---|
Lithium-ion Battery | |
Sodium-ion Battery | 160 - 180 (current), potential up to 200 - 250 |
Lithium-ion batteries store more energy in each kilogram than sodium-ion batteries. They also keep high energy density after many charges, up to 1150 Wh/L. Sodium-ion batteries have less energy density. This means they are heavier and bigger for the same energy. So, sodium-ion batteries are not the best for portable electronics or cars. But sodium-ion batteries cost less and use easy-to-find materials. They are good for storing energy from solar or wind power, where size and weight do not matter as much.
Tip: Sodium-ion batteries are a cheap choice for big energy storage projects, especially when energy density is not the most important thing.
Cycle life tells us how many times a battery can charge and discharge before it gets weaker. If a battery has a longer cycle life, you do not need to replace it as often. This saves money on repairs and new batteries. Lithium-ion batteries last longer in real use. This helps lower costs over time, even though they cost more at first.
Sodium-ion batteries wear out faster because sodium ions are bigger. This puts more stress inside the battery and can make it wear out sooner. Both types lose power over time because of chemical changes. Smart battery management systems help by controlling charging, temperature, and keeping cells balanced. These systems make batteries last longer and reduce damage.
New cathode materials and electrolytes help sodium-ion batteries last longer.
Sodium-ion batteries often need less fixing and are easier to recycle.
Smart BMS stops overcharging and deep discharge, keeping batteries healthy.
Longer cycle life means you buy new batteries less often, saving money.
As sodium-ion batteries get better, the difference in how long they last and how much they cost compared to lithium batteries will get smaller, especially for big energy storage systems.
Safety is very important for battery systems. Sodium-ion batteries are safer because of their chemistry. They use electrolytes that do not catch fire easily. They can get hotter before having problems. Their battery management systems watch charge, voltage, and temperature closely. These systems use smart programs to find and stop problems early.
Lithium batteries need more safety parts. Their chemistry can catch fire if something goes wrong. Their BMS uses extra sensors and backup systems to keep things safe. These extra parts make the system safer but also cost more.
Here is a table comparing safety features:
Safety Feature | Sodium-ion Batteries | Lithium-ion Batteries |
|---|---|---|
Thermal Runaway Temp. | Lower (~270°C), more prone to thermal runaway | |
Electrolyte Safety | Aqueous/solid-state, less flammable | Organic solvents, more flammable |
BMS Monitoring | Precise, predictive algorithms | Extensive, with redundancy for higher risk |
Sodium-ion batteries pass hard safety tests. They can handle too much charging, short circuits, crushing, and fire without catching fire. This makes them safer for homes and big storage systems.
Note: Safer batteries mean less danger for people and lower costs for safety gear.
Sodium-ion batteries are better for the environment. Sodium is easy to find in seawater and the ground. Getting sodium does not hurt nature as much as getting lithium. Making sodium batteries uses less energy and fewer bad chemicals. This means less pollution and fewer carbon emissions.
Getting sodium is less harmful than mining lithium.
Sodium batteries use simple parts, so recycling is easier and safer.
Recycling sodium batteries uses less energy and can recycle more.
Lithium battery recycling is harder, uses more energy, and makes more waste.
Sodium batteries make less carbon during making and recycling.
Scientists say sodium-ion batteries have fewer supply problems and are better for the earth. Their simple design and easy recycling make them a greener choice. Using sodium batteries helps cut down on waste and keeps the planet cleaner.
Sodium battery BMS is good for homes and small businesses. Many people pick sodium batteries because they cost less. They also work well in cold places. These batteries can run at very low temperatures, even down to -40°C. In places with cold winters, sodium batteries can save about 40% in costs compared to lithium batteries.
People use sodium battery BMS for storing solar energy at home.
Small businesses use sodium batteries for backup power.
Telecom towers use sodium batteries to work well in bad weather.
Microgrids use sodium batteries to keep power steady.
A sodium battery plant in Guangxi Province, China, gives power to 3,500 homes. It makes over 7 million kWh of clean energy every year. Sodium battery BMS charges fast and lasts for thousands of cycles. These things make sodium batteries a smart choice for energy storage in homes and businesses. They are not the best for things that need high energy density, like electric cars or small electronics.
Tip: Sodium battery BMS is safe and saves money for home and business energy storage, especially in cold places.
Big energy storage systems need batteries that last long and can be charged many times. Sodium battery BMS helps save money for grid storage because sodium is cheap and easy to find. Sodium liquid metal batteries and sodium-sulfur batteries help lower costs and support green energy. These batteries do not corrode much and can be used for big projects.
Application Scale | Cost Advantage Factors | Cycle Life Requirement | Safety & Management Complexity | Impact on Cost Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|---|---|
High-demand (Household) | Lower purchase cost; moderate cycle life; easy safety management | Moderate (4,000-5,000 cycles) | Easier to manage | Cost-effective for moderate needs; upfront cost matters most |
Large-scale Storage | Lower raw material cost; higher replacement and management costs | High (>10,000 cycles) | Complex safety and consistency control | Cost advantage reduced by frequent replacements and complex management |
Sodium battery BMS works best for smaller systems. It is easier to manage cycle life and safety in these cases. For big storage systems, you need batteries that last longer and have more safety controls. This can make costs go up. Lithium Battery BMS gives better control and can be used for bigger grid storage. It is easier to add more batteries as needed. Sodium battery BMS is still a good and green choice for many grid projects. But its benefits get smaller as the system gets bigger and more complex.
Lithium Battery BMS uses some expensive metals. Copper, cobalt, and nickel are important in the system. Copper is the current collector. Cobalt and nickel help the battery work better and last longer. These metals cost more than aluminum in sodium battery systems. The table below shows how much copper and aluminum cost:
Material | Price per kg (USD) |
|---|---|
$7 - $8 | |
Aluminum current collector | $3 - $4 |
Getting lithium, cobalt, and nickel costs a lot. Processing these metals also adds to the price. Cobalt prices change a lot and can make batteries cost 60% more. Nickel might run out in the future, so prices could go up. Recycling these metals is hard and needs special machines. This makes recycling cost more money. Most of the cost in Lithium Battery BMS comes from these metals and recycling.
Getting and processing lithium, cobalt, and nickel costs more.
Cobalt prices change fast, so planning is hard.
More people want nickel, so it might run out.
Recycling costs more because it is complicated.
Lithium Battery BMS is very common by 2025. Big companies like Samsung SDI, LG Chem, and Panasonic make billions of batteries each year. These companies use smart technology to make batteries safer and better. There are strong rules to keep batteries safe. The U.S. and EU have laws for lithium-ion batteries. These rules help make sure products work well.
The lithium-ion industry gets lots of money and support. For example, CATL and Stellantis work together to make more batteries. China makes most of the world’s lithium batteries, about 70%. This helps Lithium Battery BMS stay strong in the market. Sodium-ion batteries are new and do not have as much support or rules. Experts say Lithium Battery BMS works better and lasts longer, especially when safety matters.
Note: Lithium Battery BMS keeps getting better with new features and safety. Many industries trust it for their needs.
Recent reports say sodium battery BMS costs less and is safer. It works well for storing energy at home and in big places. The table below shows how they are different:
Feature | Sodium Battery BMS | Lithium Battery BMS |
|---|---|---|
Cost | Lower | Higher |
Safety | Higher | Medium |
Energy Density | Lower | Higher |
Cold Operation | Excellent | Limited |
Sodium battery BMS is good for homes and businesses. It is safe and does not cost much. Lithium Battery BMS is better if you need more energy in a small space. It is also good if you want something that lasts a long time. People should look at both short-term and long-term costs before picking one.
Sodium battery BMS uses aluminum and sodium. These cost less than copper and lithium. These materials are easy to find. Companies save money because they do not need rare metals. Cobalt and nickel are not needed for sodium battery BMS.
Sodium battery BMS works well in cold places. It can run at very low temperatures. It works even when it is -40°C outside. This helps homes and businesses in cold areas.
Tip: Sodium batteries help keep backup power working in winter storms.
Sodium battery BMS has strong safety features. It uses electrolytes that do not catch fire easily. It also has better thermal stability. Homeowners can trust sodium batteries to lower fire risks.
Battery Type | Typical Cycle Life (2025) |
|---|---|
Sodium-ion | 4,000 – 5,000 cycles |
Lithium-ion | 6,000 – 8,000 cycles |
Lithium battery BMS lasts longer. Sodium battery BMS costs less and is easier to recycle.